Como calcular fatoriais O valor numérico de n!D x , {\displaystyle R= (1)^ {p}\int _ {0}^ {n}f^ { (p1)} (x) {B_ {p1} (x\lfloor x\rfloor ) \over (p1)!}\,dx,} donde B i ( x − ⌊ x ⌋ ) {\displaystyle B_ {i} (x\lfloor x\rfloor )}è il fattoriale di Può essere calcolato anche facendo ricorso al triangolo di TartagliaEsso fornisce il numero delle combinazioni semplici di elementi di classe Per esempio =!!()!
Just Need Help Finding The A 3 N General Formula Chegg Com
What is n*(n+1)/2
What is n*(n+1)/2-John Baez () "My Favorite Numbers 24" (PDF) The EulerMaclaurin formula, Bernoulli numbers, the zeta function, and realvariable analytic continuation by Terence TaoLa somma di tutti i numeri naturali, anche scritta 1 2 3 4 o mediante il simbolo di sommatoria come ∑ n = 1 ∞ n {\displaystyle \sum _{n=1}^{\infty }n} è una serie divergente ;




Tulip Fabric Dye 2 N 1 Formula Black Tulip Color
Don't miss a Formula 1 moment – with the latest news, videos, standings and results Go behind the scenes and get analysis straight from the paddockDemostración de x n algebraico Dando (ab) n = (n, 0) a n b 0 (n, 1) a (n1) b 1 (n, 2) a (n2) b 2 (n, n) a 0 b n Aquí (n,k) es el coeficiente 12 An approximation is good enough Since phi is less than one in size, its powers decrease rapidly We can use this to derive the following simpler formula for the nth Fibonacci number F (n) F (n) = round ( Phi n / √5 ) provided n ≥ 0 where the round function gives the nearest integer to its argument
Die Formel gilt auch für ungerade n Die mittlere Zahl hat keinen Partner bei der Paarbildung Man bildet also (n1)/2 Paare mit der jeweiligen Summe (n1), addiert die mittlere Zahl (n1)/2 und kommt so ebenfalls auf diese SummenformelLEGENDRE POLYNOMIALS AND APPLICATIONS 3 If λ = n(n1), then cn2 = (n1)n−λ(n2)(n1)cn = 0 By repeating the argument, we get cn4 = 0 and in general cn2k = 0 for k ≥ 1 This means • if n = 2p (even), the series for y1 terminates at c2p and y1 is a polynomial of degree 2pThe series for y2 is infinite and has radius of convergence equal to 1 and y2 is unbounded • If n = 2p 1Lamb E (14), "Does 123Really Equal –1/12?", Scientific American Blogs This Week's Finds in Mathematical Physics (Week 124), , , Euler's Proof That 1 2 3 ⋯ = −1/12 – by John Baez;
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreIn matematica, il coefficiente binomiale (che si legge "su ") è un numero intero non negativo definito dalla seguente formula = (;) =!!= 5 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 = 1 {\displaystyle 5!=5\cdot 4\cdot 3\cdot 2\cdot 1=1\,} The value of 0!




Problem 38 Sebastian Martin Ruiz Prime Formulas




Gamma Function Wikipedia
= = In overeenstemming met de definitie van het lege product is afgesproken dat !Fórmulas de Matemática As fórmulas matemáticas representam uma síntese do desenvolvimento de um raciocínio e são constituídas por números e letras Conhecêlas é necessário para resolver muitos problemas que são cobrados em concursos e no Enem, principalmente por reduzir, muitas vezes, o tempo de resolução de uma questãoHallar el t ermino general y estudiar su naturaleza Soluci on Aplicamos la f ormula a n= S n S n 1 y obtenemos a n= 5n2 3n 2 n2 1 5(n 1)2 3(n




Find S N In Terms Of N Mathematics Stack Exchange




Find Formulas For The Average And Sd Of 1 2 3 N Chegg Com
= n ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋯ ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 {\displaystyle n!=n\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdots \cdot 3\cdot 2\cdot 1\,} For example, 5 !Dados m elementos, a 1, a 2, a 3, a m, se llama combinación naria, o de orden n, a los conjuntos formados por n elementos elegidos entre ellos, de modo queEl término de error El término de error R es R = ( − 1 ) p ∫ 0 n f ( p 1 ) ( x ) B p 1 ( x − ⌊ x ⌋ ) ( p 1 ) !




Suppose T N Is Defined Recursively As Follows T N Chegg Com




Find A Formula For The Following 6 7 8 Chegg Com
La somma dei primi n {\displaystyle n} termini della serie può essere trovata con la formula n ( n 1 ) 2 {\displaystyle {\frac {n(n1)}{2}}}Elle prolonge la fonction factorielle à l'ensemble des nombres complexes (à l'exception des entiers négatifs) on a pour tout entier n > 0 Γ(n) = (n–1)! Explanation using the method of proof by induction this involves the following steps ∙ prove true for some value, say n = 1 ∙ assume the result is true for n = k ∙ prove true for n = k 1 n = 1 → LH S = 12 = 1 and RHS = 1 6 (1 1)(2 1) = 1 ⇒result is true for n = 1




1 Existe Una Formula Para Calcular La Suma 1 4 9 N Sabiendo




A Short Explanation Of Le Mystere D Urbicande Francois Schuiten Benoit Peeters
Die Gaußsche Summenformel (nicht zu verwechseln mit einer Gaußschen Summe), auch kleiner Gauß genannt, ist eine Formel für die Summe der ersten aufeinanderfolgenden natürlichen Zahlen 0 1 2 3 4 ⋯ n = ∑ k = 0 n k = n ( n 1 ) 2 = n 2 n 2 {\displaystyle \dotsb n=\sum _{k=0}^{n}k={\frac {n(n1)}{2}}={\frac {n^{2}n}{2}}}Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreN de t ermino general a n= n( 1) n2 2n Soluci on Como l m n(n 1) n2 2n = 1 6= 0, la serie es divergente 2 Sabiendo que la suma de los nprimeros t erminos de una serie es S n= 5n2 3n 2 n2 1;




Quartile Formula Calculation Of Quartile Examples And Excel Template



Suma De Los Primeros Numeros Naturales Formula Demostracion Y Ejemplos 1 2 3 N Youtube
) indica la multiplicación de todos los números enteros desde un número dado, descendiendo hasta el número 1 "4!" normalmente se pronuncia "4 factorial" También se puede decir "factorial de 4"= De faculteitsfunctie groeit snel, zelfs sneller dan een exponentiële functieDokaz formule za parcijalnu sumu Dokaz da je sum prirodnih brojeva do n () može se dokazati na mnoštvo načina Najprije, neka je = Članovi se mogu pregrupisati i napisati od Euler's Proof That 1 2 3 =




Program For Factorial Of A Number Geeksforgeeks




Matematicas Para Ver Y Tocar
Excel in math and science Log in with Facebook Log in with Google Log in with email Join using Facebook Join using Google Join using email2 Fíjate que si k = 1 lo que nos sale es la fórmula del término general wwwcajondecienciascom Cajón de Ciencias Veamos el ejemplo 2 Ahora nos falta conocer a1 y la diferencia Por lo tanto, usaremos dos veces la fórmula anterior;Sa nième somme partielle est donc le nombre triangulaire S n = 1 2 n, égal à n(n 1)/2 La suite (S n) tend vers l'infini la série n'est donc pas convergente Elle ne possède donc pas de somme au sens usuel du terme Elle n'est pas non plus sommable au sens de Cesàro



Which Of The Following Transition In Hydrogen Atoms Emits Photon




Data Structures Sorting Haim Kaplan Uri Zwick December
Lassen sich die Binomialkoeffizienten ( n k ) {\displaystyle \textstyle {\binom {n} {k}}} auch durch folgende Rekursionsvorschrift ermitteln ( n 0 ) = 1 = ( n n ) {\displaystyle {\binom {n} {0}}=1= {\binom {n} {n}}} für alle n ≥ 0 {\displaystyle n\geq 0} For T(n)=123n we take two copies and get a rectangle that is n by (n1) So there you have it our visual proof that T(n) = 1 2 3 n = n(n 1)/2Además, es fácil ver que si el cuadrado perfecto es el cuadrado de




Just Need Help Finding The A 3 N General Formula Chegg Com




Demostrar Una Formula Por Induccion Matematica Ejercicio 1 Youtube
= 1×2××(n–1) Sommaire 1 DéfinitionPode ser calculado por multiplicação repetida se n não for grande demais É isto que as calculadoras fazem O maior fatorial, que a maioria dasResultado es cierto para los casos iniciales n=1, para el que n2=1 da resto 1 al dividir por 4, y para n=2, para el que n2=4 da resto 0 al dividir por 4 Claramente podemos llegar a cualquier entero positivo par dando saltos de 2 en 2, desde n=2, y para cualquier entero positivo impar dando saltos de 2 en 2, desde n=1, así que, ¡ya está!



Approximations For The Factorial Function



Search Q Factorial Formula Tbm Isch
DE LO QUE SE DEDUCE QUE S n será un polinomio de tercer grado si n=1, P (n)= 1 si n=2, P (n)=5 si n=3, P (n)=14 si n=4, P (n)=30 se despejan los términos y sale que A=1/3 B=1/2 C=1 Transcript Prove 1 2 3 n = (n(n1))/2 for n, n is a natural number Step 1 Let P(n) (the given statement)\ Let P(n) 1 2 3 n = (n(n1))/2 Step The home page for the official website of the FIA Formula 2 Championship The Road to F1




Useful Formulas Plh Px Bn Sin Un Cos N 1 Fs Chegg Com




6 A Use The Binomial Formula And De Moivre S Chegg Com
IDENTITÉS REMARQUABLES & Formules à noter de degré supérieur à 2 Identités remarquables en puissance n Voir Développements, notamment usage en numération Vocabulaire on parle d'identités ou de formules remarquables ou moins remarquables Développement "magique" avec les coefficients polynomiaux Pour développer (a b)n ouIn mathematics, the factorial of a nonnegative integer n, denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n n !Use the N function to convert value to a number Values are converted according the the following table In most cases, using the N function is unnecessary, because Excel automatically converts values when needed The N function is provided for compatibility with other spreadsheet programs




Pdf Partial Sum For An Alternating Series Involving The Reciprocals Of Logarithms First Summation Formula




How To Derive N 1 2 From 1 2 3 N N Quora
Os fatoriais são também frequentemente utilizados como exemplos simplificados de recursividade, em ciência da computação, porque satisfazem as seguintes relações recursivas (se n ≥ 1) n!Voor bijvoorbeeld = is !Mas genericamente, chamase sequência de Fibonacci qualquer função g tal que g(n 2) = g(n) g(n 1) Essas funções são precisamente as de formato g(n) = aF(n) bF(n 1) para alguns números a e b, então as sequências de Fibonacci formam um espaço vetorial com as funções F(n) e F(n 1) como base




All Maths Formulas From Sine Circle



What Is The Reduction Formula Of The Integration Of Sin Nx Dx From Limit 0 To Pi 2 Quora
Si la fórmula n(n 1) 2 nos permite calcular la suma de los n primeros números naturales, ¿cuánto es la suma de todos los números primos y compuestos desde 1 hasta 100?Definición por producto e inducción Podemos definir el factorial de un número entero positivo n, expresado n!, como el producto de todos los números enteros positivos menores o iguales que n n ! The way the items are ordered now you can see that each of those pairs is equal to N (N11 is N, N22 is N) Since there are N1 items, there are (N1)/2 such pairs So you're adding N (N1)/2 times, so the total value is N*(N1)/2




N 1 2 Formula For Finding Median Mth 3052 Youtube




De Moivre S Theorem Provides An Explicit Formula To Chegg Com
Die F1 auf Formel1de Formel 1 live, Formel1Ergebnisse, Formel1Termine, F1News und Formel1Fahrer und TeamsLa formule de Stirling 1) On commence par la présentation classique d'une épreuve de concours où on ne découvre pas le résultat Pour n ∈ N∗, on pose un = n! To sum integers from 1 to N, start by defining the largest integer to be summed as N Don't forget that integers are always whole and positive numbers, so N can't be a decimal, fraction, or negative number Once you've defined the integer value of N, use the formula sum = (N × (N1)) ÷ 2 to find the sum of all the integers between 1 and N!




Codigo De Macro En Excel Para Evaluar La Formula N Esima Del Factor De Download Scientific Diagram



S N N 1 2 Solve For N Youtube
(n faculteit), is het product van de getallen tot en met !La función factorial (símbolo !De faculteit van een natuurlijk getal, genoteerd als !



Derive A Formula For The Integral Of Cosn X Stumbling Robot
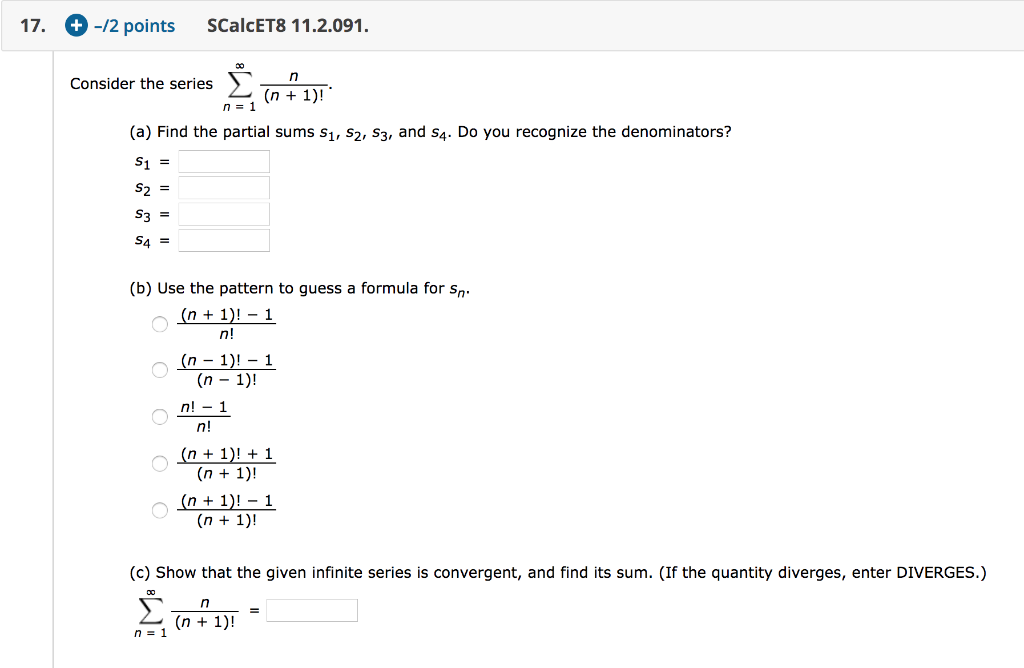



17 2 Points Scalcet8 11 2 091 Consider The Chegg Com
EJERCICIOS DE SUCESIONES NUMERICAS 1 C alculo de l mites 1 Calcular el l mite de la sucesi on de t ermino general a n= p n2 4n p n2 n Soluci on Multiplicamos y dividimos por el conjugado yFind N(4(benzodthiazol2yl)phenyl) and related products for scientific research at MilliporeSigmaA a are as follows ∑ k = 1 n k = n ( n 1) 2 ∑ k = 1 n k 2 = n ( n 1) ( 2 n 1) 6 ∑ k = 1 n k 3 = n 2 ( n 1) 2 4 \begin {aligned} \sum_ {k=1}^n k &= \frac {n (n1)}2 \\ \sum_ {k=1}^n k^2 &= \frac {n (n1) (2n1)}6 \\ \sum_ {k=1}^n k^3 &= \frac {n^2 (n1)^2}4 \end {aligned} k=1∑n k k=1∑n k2 k=1∑n



2




Gamma Function Wikipedia
Is 1, according to the convention for an= = = Recursief geldt dus voor de faculteit != 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 × × ( n − 1 ) × n {\displaystyle n!=1\times 2\times 3\times 4\times \times (n1)\times n



Search Q Newton Formula Tbm Isch




1234n Formula
Find N(4chlorophenyl)2(4phenyl1piperazinyl)acetamide and related products for scientific research at MilliporeSigmaDe somformule van Gauss is een formule om de som van de eerste n {\displaystyle n} opeenvolgende natuurlijke getallen te bepalen 1 2 3 4 n = ∑ k = 1 n k = n ( n 1 ) 2 {\displaystyle 1234\ldots n=\sum _ {k=1}^ {n}k= {\frac {n (n1)} {2}}}= n (n − 1)!




Brilliant Org Triangular Numbers Dots Pattern Dots




1234n Formula
De exemplu, folosind funcția zeta Riemann se obține rezultatul paradoxal = În cazul particular al primelor n numere naturale, suma 1 2 3 n este ușor calculabilă = = () Suma respectivă este numită și suma luiLa primera, para calcular la diferencia an = ak (nA) 5049 B) 5050 C) 5051 D) E)



Approximations For The Factorial Function




Induction Chapter 4 1 Some Slides Have Been
N e n √ n On veut montrer que la suite (un)n∈N∗ convergeet a pour limite un réel strictement positif K Pour cela, on pose pour n ∈ N∗, vn =ln(un)puis wn =vn1 −vn




Factorial Wikipedia
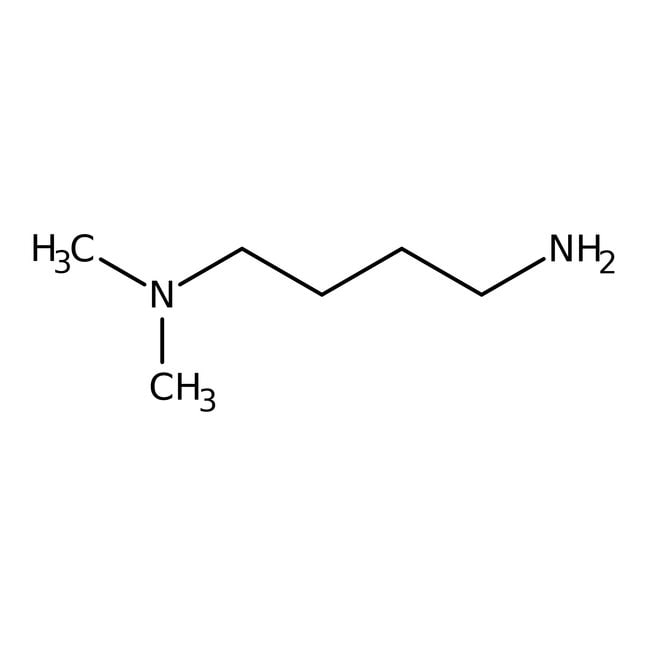



Alfa Aesar N N Dimethyl 1 4 Butanediamine 98 Tertiary Amines Amines Fisher Scientific



Approximations For The Factorial Function




Is There Any Elementary Formula For The Sequence Sum K 1 N Left 2k 1 Right Left Frac 1 2 Right K Mathematics Stack Exchange




Compute The Following Sums 1 3 5 7 Chegg Com




What Is This Formula N N 1 2 Please Tell The Answer Brainly In



Www Jstor Org Stable
/what-is-the-rydberg-formula-604285_final-251d1441e24e44c88aab687409554ed4.png)



What Is The Rydberg Formula And How Does It Work




Formula N 5 1 Zu De Do B M N 1 1 Chegg Com



2




1234n Formula
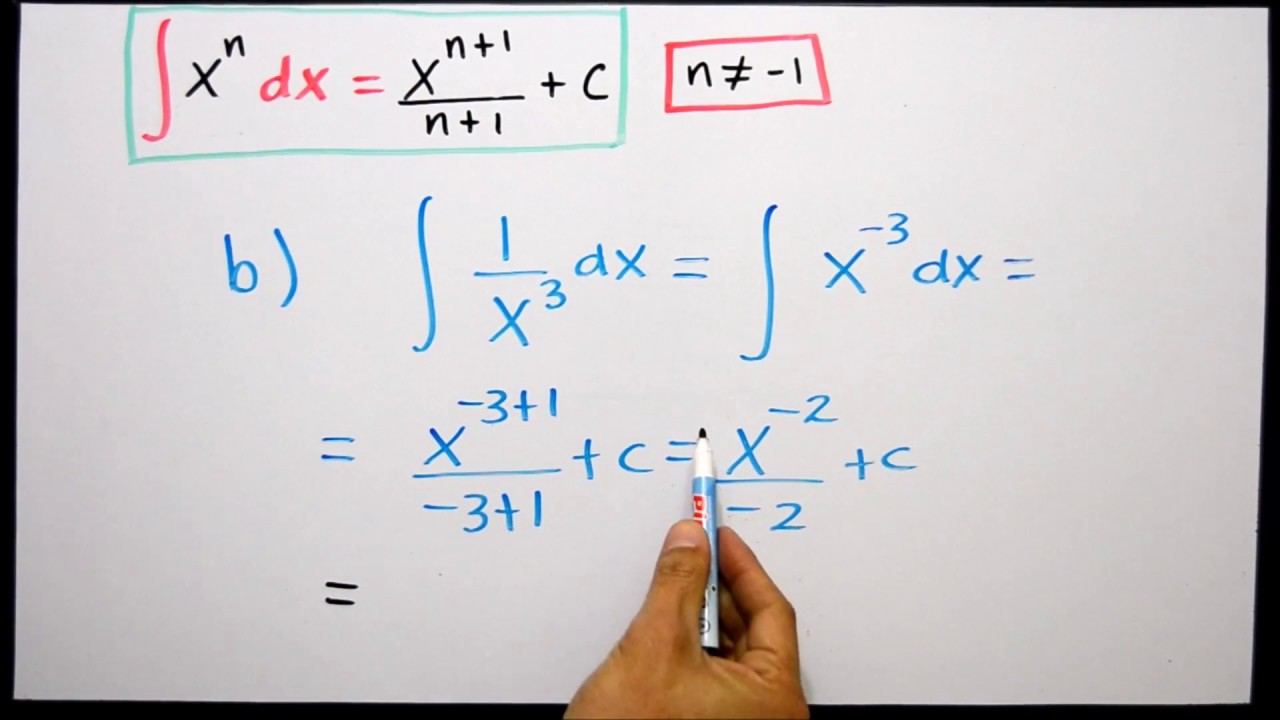



Ci 02 Integral De X A La N Cuatro Ejemplos Resueltos Paso A Paso Youtube



Http Petermc Net Maths Math116 Hayman Pdf




Chapter 7 Exercises
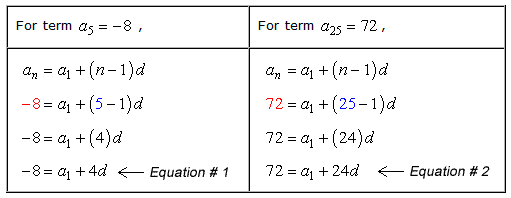



Arithmetic Sequence Formula Chilimath




D8g31znxgu36jm




Sumatorias Con Muchas Iteraciones Formulas De Sumatoria Parte 1 Youtube




How To Find How Many Diagonals Are In A Polygon 11 Steps



Regla Del Equipo De Dos Pizzas Two Pizza Team Apuntes De Programacion
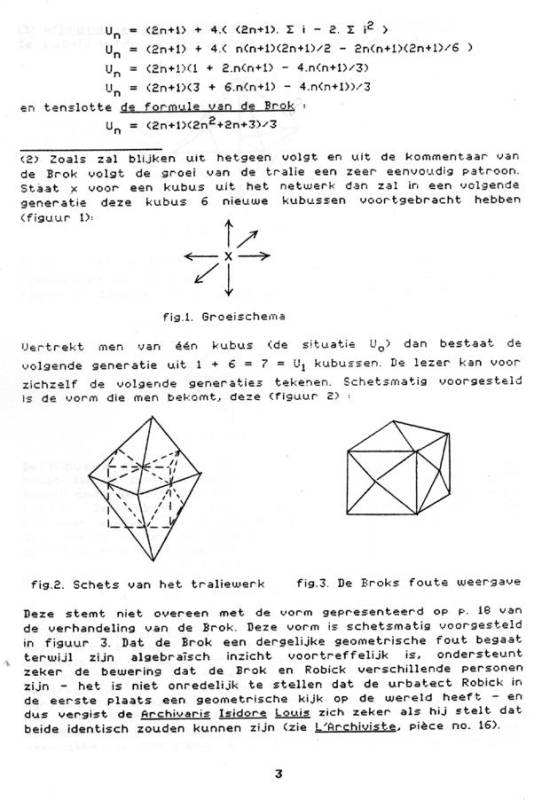



A Short Explanation Of Le Mystere D Urbicande Francois Schuiten Benoit Peeters



S N N 1 2 Solve For N Youtube




Epa1 New Crystal Modifications Of A Yellow Disazo Colorant And A Process For Their Production Google Patents



Permutations




Factorial Wikipedia



Decile Formula Calculation Of Decile Examples With Excel Template



Octadecanamide N N 1 2 Ethanediylbis 12 Hydroxy Sielc




1234n Formula




Problem 3 A Find A Formula For 23 3 4 N N1 We Have Chegg Com




Factorial Wikipedia




5 Recurrences Some Of The Following Questions Ask Chegg Com




1 2 2 3 3 4 N N 1 Formula Novocom Top




De Moivre Theorem For Fractional Power K N Explanation Mathematics Stack Exchange
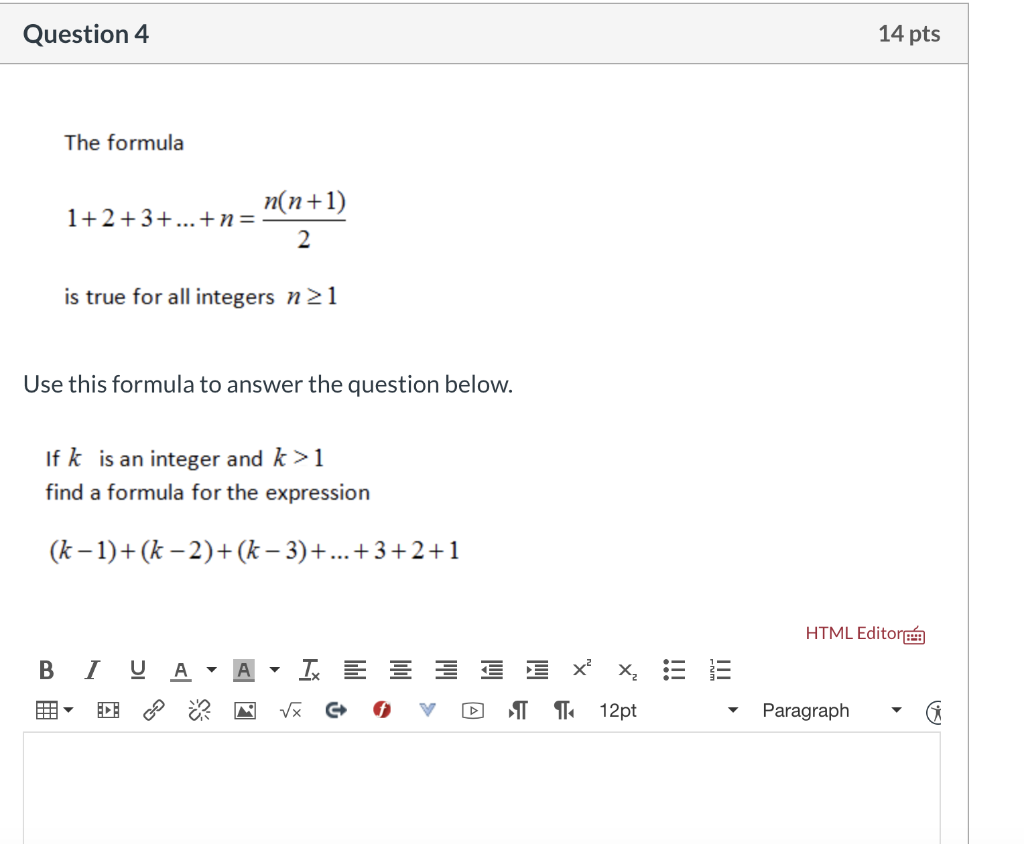



Question 4 14 Pts The Formula N N 1 1 2 3 N 2 Chegg Com




Pdf Further Summation Formulas For The Kamp E De F Eriet Function




Sands807




Solved N 1 N N 1 2n 1 N 2 Prove Summation Formula Induction Q




1 2 3 4 Wikipedia




1 2 2 3 3 4 N N 1 Formula Novocom Top




Gamma Function Wikipedia



Stemjock Com Stem books Churchill complex variables 8e Chapter 1 Section 8 Exercise 11 Churchillcv8es8e11 Pdf
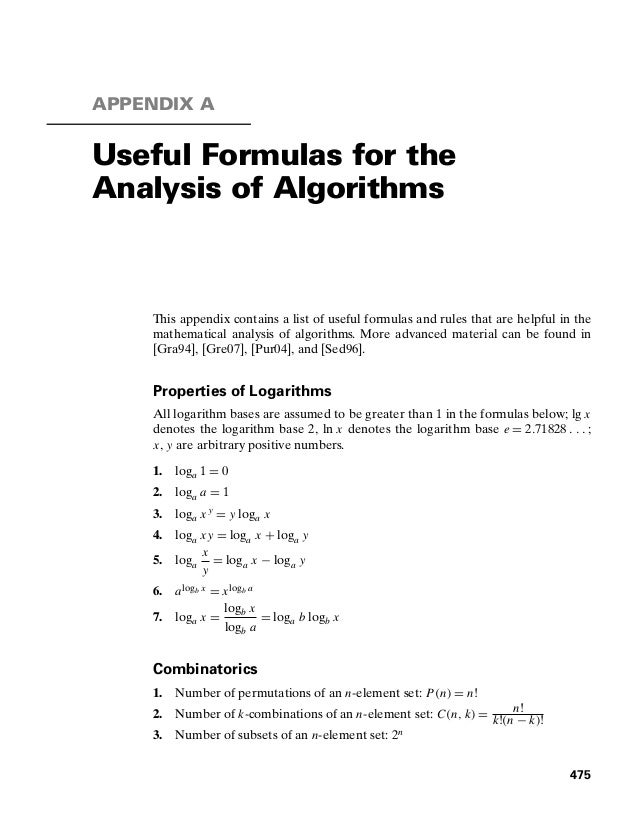



Formulas Para Algoritmos



1




Catalan Number Wikipedia




Wallis Product Wikipedia




Tulip Fabric Dye 2 N 1 Formula Black Tulip Color



2




Pdf A New Formula For The Nth Prime Sebastian Ruiz Academia Edu




Problem 3 A Find A Formula For 1 2 2 33 4 N N 1 We Chegg Com




Epa1 New Crystal Modifications Of A Yellow Disazo Colorant And A Process For Their Production Google Patents




Derangement Wikipedia




Codigo De Macro En Excel Para Evaluar La Formula N Esima Del Factor De Download Scientific Diagram



Solved Definite Integral And The Wallis Formula Course Hero



2




1234n Formula




Binomial Coefficient Wikipedia




Formula Sheet Summary Advanced Engineering Mathematics The Alternative Notation For The Exponential Function Ex Exp Euler Formula Ejx Cos Sin De Moivre Studocu



Solved Definite Integral And The Wallis Formula Course Hero
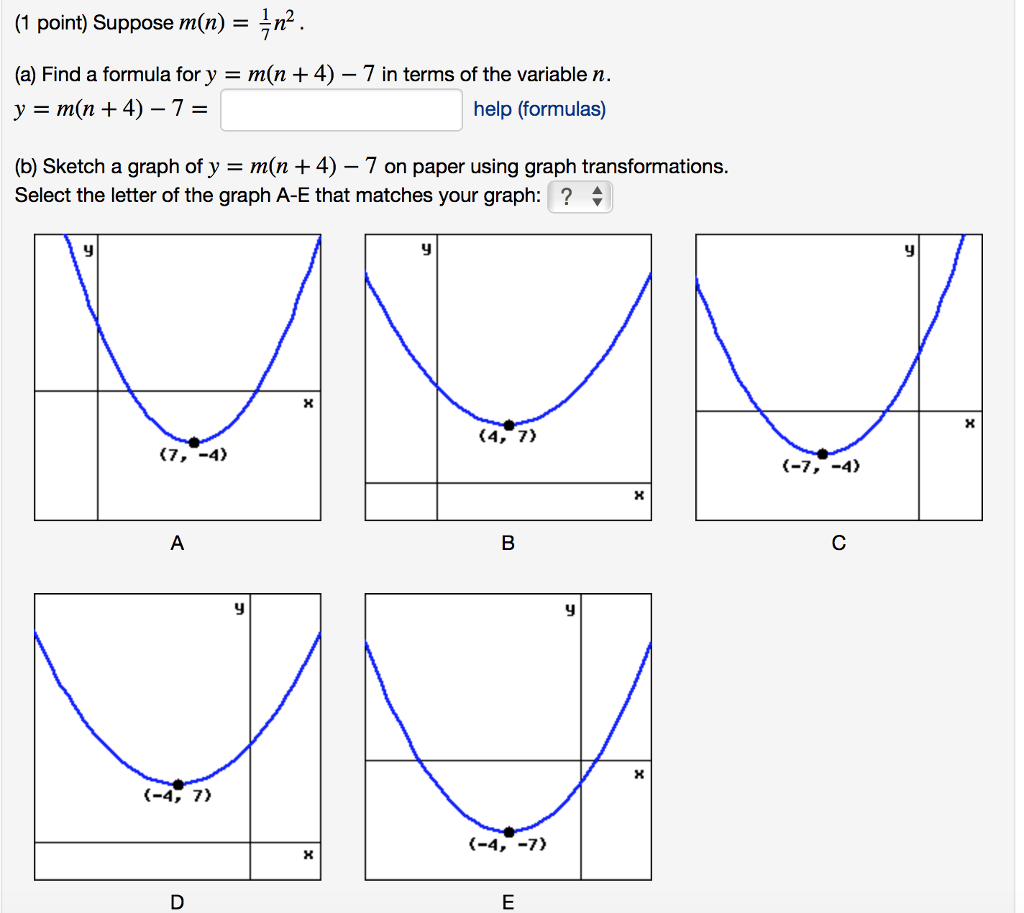



Suppose M N 1 7 N 2 A Find A Formula For Y Chegg Com




11 1 A Write The Sigma Notation Formula For The Chegg Com



2




Analysis Of Algorithms Ii Ppt Video Online Download




Document



1




1 2 3 4 Wikipedia




Series Y Sumatorias Formulas Metodos Y Ejemplos De Razonamiento Matematico Preuniversitario Y Secundaria Pdf



Tie Dye Your Summer Tulip Fabric Dye 2 N 1 Formula Aqua



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿